In computer programming, we use the if statement to run a block code only when a certain condition is met.
For example, assigning grades (A, B, C) based on marks obtained by a student.
- if the percentage is above 90, assign grade A
- if the percentage is above 75, assign grade B
- if the percentage is above 65, assign grade C
Learn Python with Challenges
Solve challenges and become a Python expert.
In Python, there are three forms of the if...else statement.
ifstatementif...elsestatementif...elif...elsestatement
1. Python if statement
The syntax of if statement in Python is:
if condition:
# body of if statement
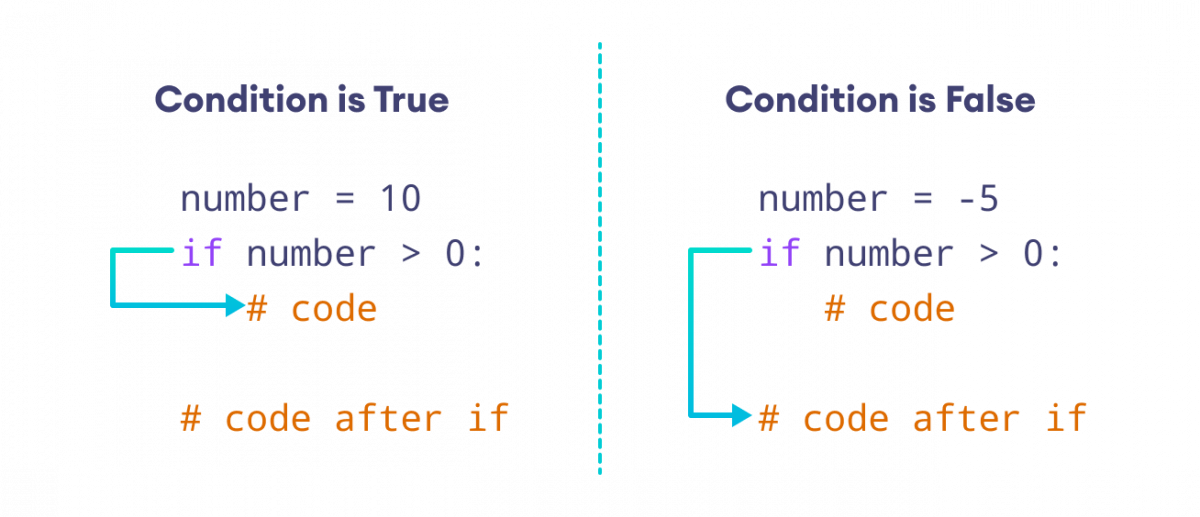
The if statement evaluates condition.
- If
conditionis evaluated toTrue, the code inside the body ofifis executed. - If
conditionis evaluated toFalse, the code inside the body ofifis skipped.
Example 1: Python if Statement
number = 10
# check if number is greater than 0
if number > 0:
print('Number is positive.')
print('The if statement is easy')
Output
Number is positive. The if statement is easy
In the above example, we have created a variable named number. Notice the test condition,
number > 0
Here, since number is greater than 0, the condition evaluates True.
If we change the value of variable to a negative integer. Let's say -5.
number = -5
Now, when we run the program, the output will be:
The if statement is easy
This is because the value of number is less than 0. Hence, the condition evaluates to False. And, the body of if block is skipped.
2. Python if...else Statement
An if statement can have an optional else clause.
The syntax of if...else statement is:
if condition:
# block of code if condition is True
else:
# block of code if condition is False
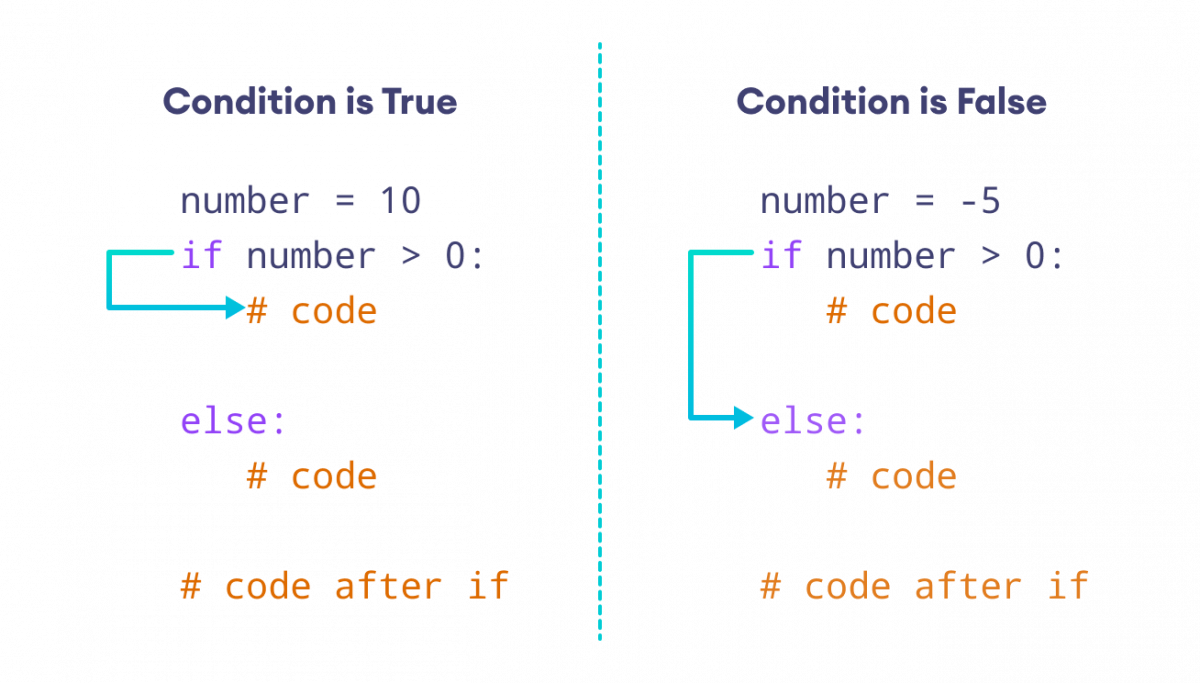
The if...else statement evaluates the given condition:
If the condition evaluates to True,
- the code inside
ifis executed - the code inside
elseis skipped
If the condition evaluates to False,
- the code inside
elseis executed - the code inside
ifis skipped
Example 2. Python if...else Statement
number = 10
if number > 0:
print('Positive number')
else:
print('Negative number')
print('This statement is always executed')
Output
Positive number This statement is always executed
In the above example, we have created a variable named number. Notice the test condition,
number > 0
Since the value of number is 10, the test condition evaluates to True. Hence code inside the body of if is executed.
If we change the value of variable to a negative integer. Let's say -5.
number = -5
Now if we run the program, the output will be:
Number is negative. This statement is always executed.
Here, the test condition evaluates to False. Hence code inside the body of else is executed.
3. Python if...elif...else Statement
The if...else statement is used to execute a block of code among two alternatives.
However, if we need to make a choice between more than two alternatives, then we use the if...elif...else statement.
The syntax of the if...elif...else statement is:
if condition1:
# code block 1
elif condition2:
# code block 2
else:
# code block 3
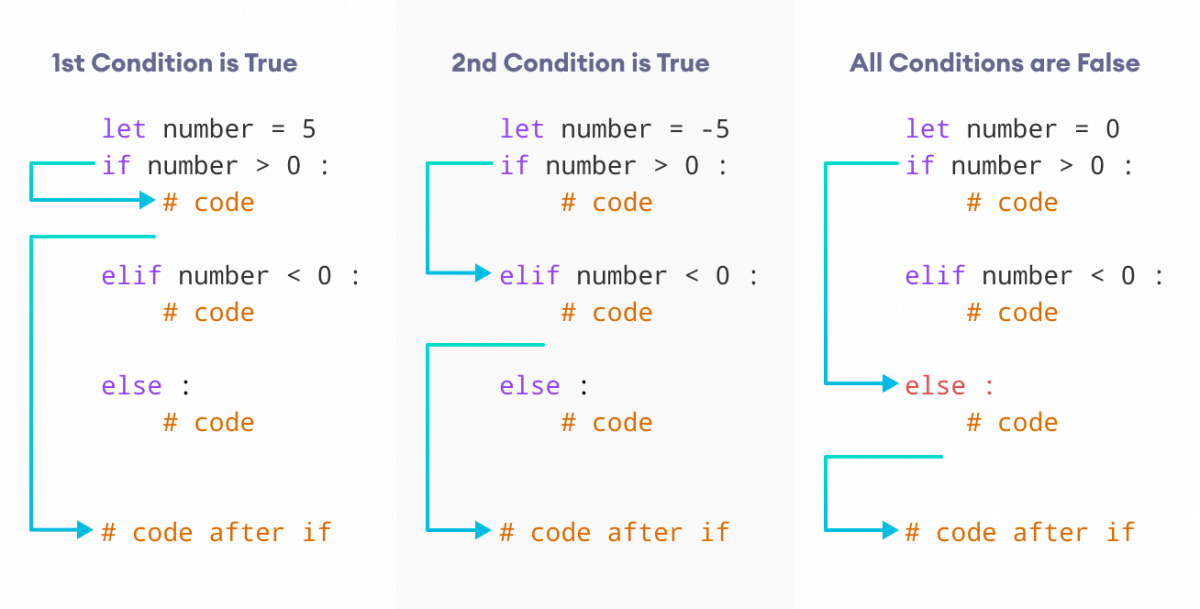
Here,
- If condition1 evaluates to
true, code block 1 is executed. - If condition1 evaluates to
false, then condition2 is evaluated.- If condition2 is
true, code block 2 is executed. - If condition2 is
false, code block 3 is executed.
- If condition2 is
Example 3: Python if...elif...else Statement
number = 0
if number > 0:
print("Positive number")
elif number == 0:
print('Zero')
else:
print('Negative number')
print('This statement is always executed')
Output
Zero This statement is always executed
In the above example, we have created a variable named number with the value 0. Here, we have two condition expressions:
Here, both the conditions evaluate to False. Hence the statement inside the body of else is executed.
Python Nested if statements
We can also use an if statement inside of an if statement. This is known as a nested if statement.
The syntax of nested if statement is:
# outer if statement
if condition1:
# statement(s)
# inner if statement
if condition2:
# statement(s)
Notes:
- We can add
elseandelifstatements to the innerifstatement as required. - We can also insert inner
ifstatement inside the outerelseorelifstatements(if they exist) - We can nest multiple layers of
ifstatements.
Example 4: Python Nested if Statement
number = 5
# outer if statement
if (number >= 0):
# inner if statement
if number == 0:
print('Number is 0')
# inner else statement
else:
print('Number is positive')
# outer else statement
else:
print('Number is negative')
# Output: Number is positive
In the above example, we have used a nested if statement to check whether the given number is positive, negative, or 0.