In SQL, it's possible to place a SQL query inside another query. This inner query is known as a subquery.
Example
-- use a subquery to select the first name of customer
-- with the maximum value of customer id
SELECT first_name
FROM Customers
WHERE customer_id= (
SELECT MAX(customer_id)
FROM CUSTOMERS
);Here, the query is divided into two parts:
- the subquery selects the maximum id from the Customers table
- the outer query selects the first_name of the customer with the maximum id (returned by the sub query)
SQL Subquery Syntax
The syntax of SQL subqueries is:
SELECT column FROM table
WHERE column OPERATOR (
SELECT column FROM table
);
Here,
columnis the name of the column(s) to filterOPERATORis any SQL operator to connect the two queriestableis the name of the table to fetch the column from
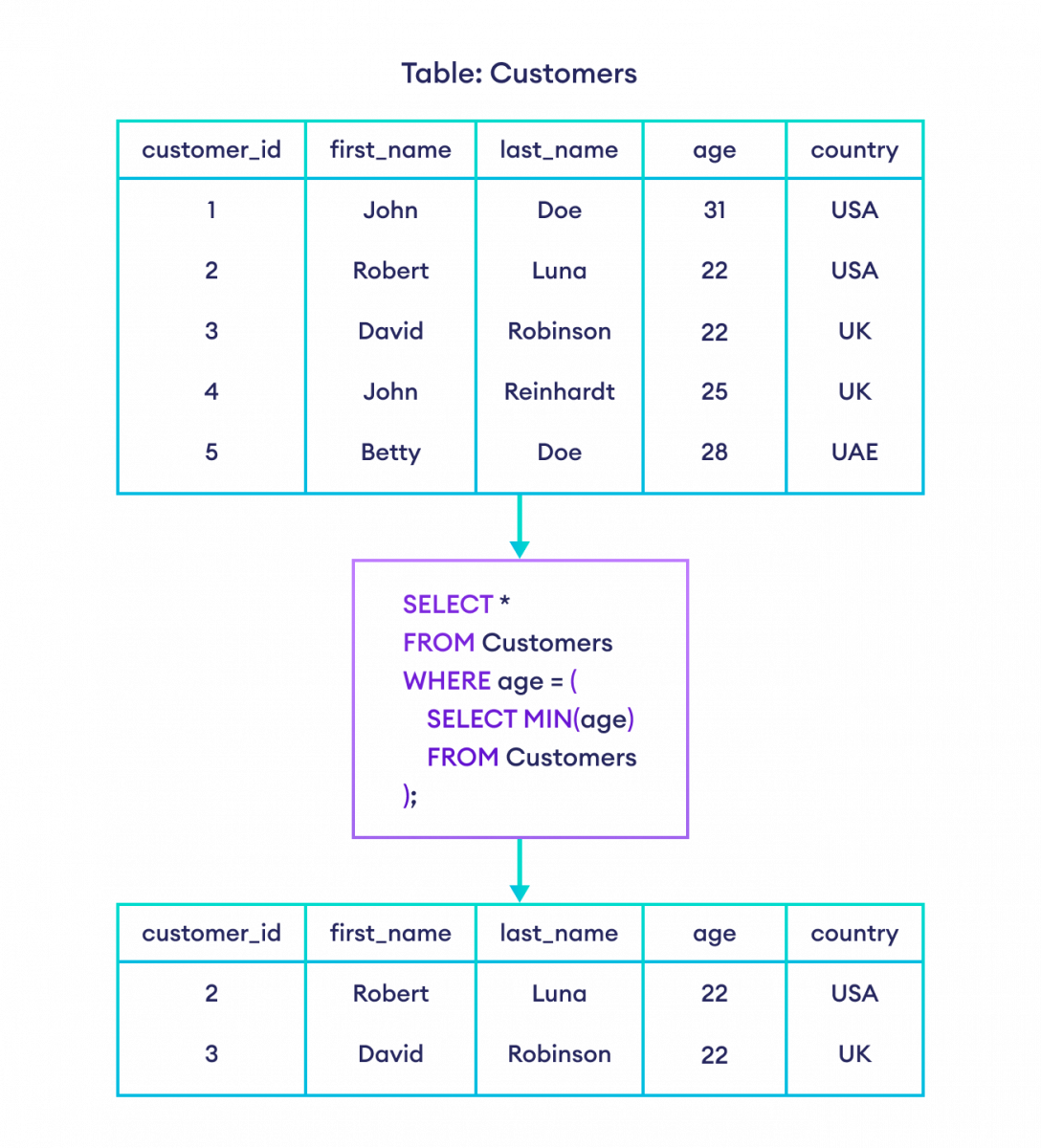
Example 1: SQL Subquery
-- select all the rows from the Customers table with the minimum age
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE age = (
SELECT MIN(age)
FROM Customers
);In a subquery, the outer query's result depends on the result set of the inner subquery. That's why subqueries are also called nested queries.
Here, the SQL command
- executes the subquery first; selects the minimum age from the Customers table.
- executes the outer query; selects the rows where age is equal to the result of subquery.
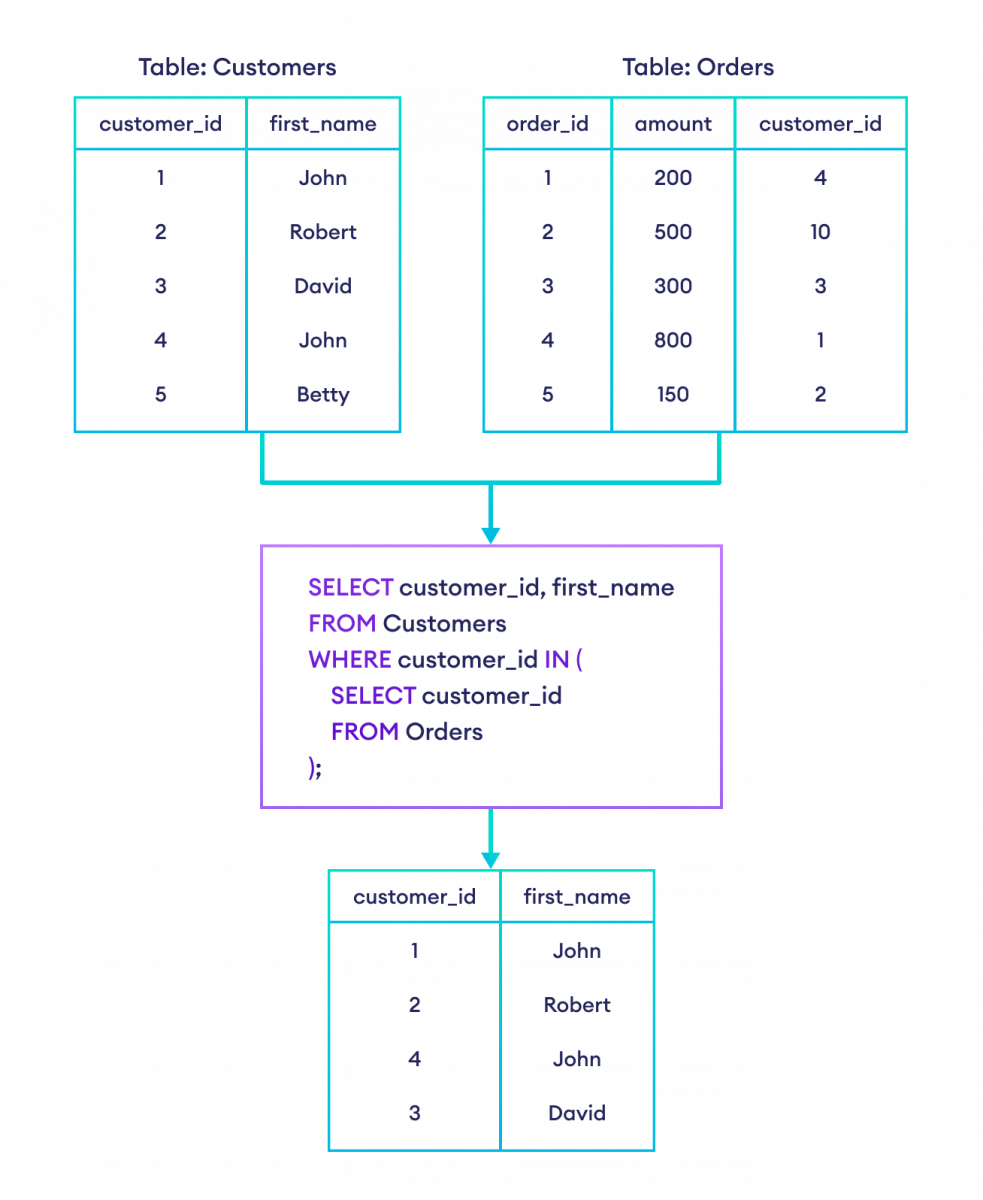
Example 2: SQL Subquery With IN Operator
Suppose we want the details of customers who have placed an order. Here's how we can do that using a subquery:
-- select the customers who have made orders
SELECT customer_id, first_name
FROM Customers
WHERE customer_id IN (
SELECT customer_id
FROM Orders
);Here, the SQL command
- selects customer_id from the Orders table
- select those rows from the Customers table where customer_id is in the result set of the subquery
SQL Subquery and JOIN
In some scenarios, we can get the same result set using a subquery and the JOIN clause. For example,
-- SELECT DISTINCT only selects the unique combination of customer_id and first_name
-- join the Customers and Orders tables and select the rows where their customer_id values match
-- result set contains customer_id and first_name of customers who made an order
SELECT DISTINCT Customers.customer_id, Customers.first_name
FROM Customers
INNER JOIN Orders
ON Customers.customer_id = Orders.customer_id
ORDER BY Customers.customer_id;The result set of the above query will be the same as the one below:
-- display the distinct customer ids and first names
-- of customers who made an order using a subquery
SELECT customer_id, first_name
FROM Customers
WHERE customer_id IN (
SELECT customer_id
FROM Orders
);Note: We should use the JOIN clause instead of a subquery whenever possible. It's because the execution speed of JOIN is more optimized than that of a subquery.