The SQL CASE statement evaluates a list of conditions one-by-one and returns a value based on that condition.
Example
-- add a new column named 'amount_category' in the output
-- store 'High' where the amount is 10000 or higher
-- store 'Low' where the amount is less than 10000
SELECT order_id, item, amount,
CASE
WHEN amount >= 10000 THEN 'High'
WHEN amount < 10000 THEN 'Low'
END AS amount_category
FROM Orders;SQL CASE Syntax
The SQL CASE statement has the following syntax:
SELECT column1, column2,... ,
CASE
WHEN condition THEN result
END AS Alias
FROM table;
Here,
column1,column2, ...are the names of the columns to be included in the result setCASEchecks theconditionresultis the result or value to be inserted to the new column ifconditionis satisfiedENDends theCASEstatementAS Aliasspecifies theAliasname for the new columntableis the name of the table.
Note: The syntax of CASE always starts with the CASE keyword and ends with the END keyword followed by a column name alias.
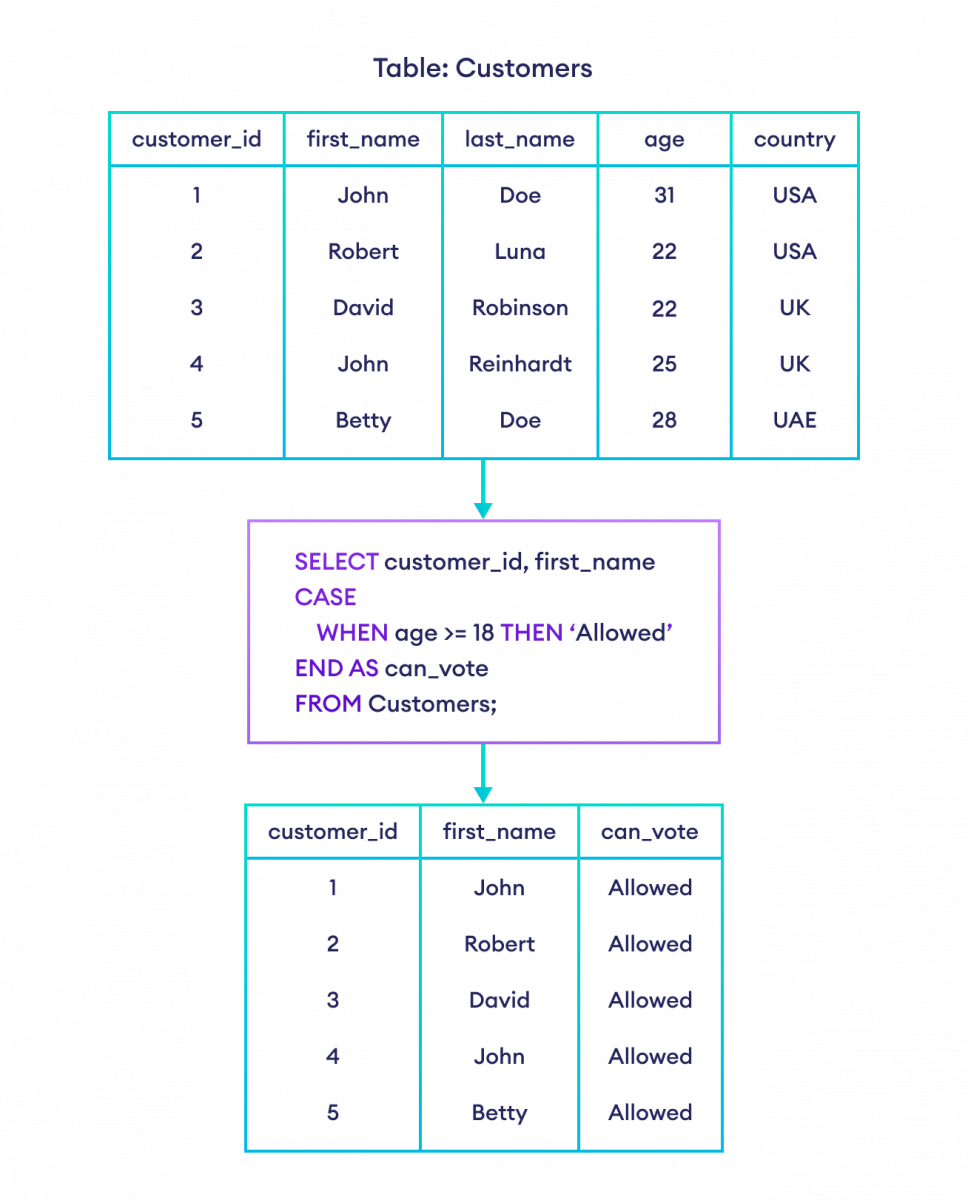
Example 1: SQL CASE
-- add a new column 'can_vote' to Customers table
-- insert 'Allowed' into it if customer is older than 17
SELECT customer_id, first_name,
CASE
WHEN age >= 18 THEN 'Allowed'
END AS can_vote
FROM Customers;Here, the SQL command checks each row with the given case. The result set contains
- columns with customer_id and first_name with their values
- Allowed in the can_vote column for rows whose age is greater than or equal to 18.
Example 2: SQL CASE Statement
Let's take a look at another example where we want to provide a 10% discount on each order for a Christmas sale if the amount is 400 or more.
SELECT order_id, customer_id,
CASE
WHEN amount >= 400 THEN (amount - amount * 10/100)
END AS offer_price
FROM Orders;Here, the SQL command checks if the amount is greater than or equal to 400. If this condition is satisfied, a new column offer_price will contain the values equal to amount - amount*10/100.
SQL CASE With Multiple Conditions
It is also possible to stack multiple conditions inside a single CASE clause.
-- multiple CASE conditions in SQL
SELECT customer_id, first_name,
CASE
WHEN country = 'USA' THEN 'United States of America'
WHEN country = 'UK' THEN 'United Kingdom'
END AS country_name
FROM Customers;Here, the result set will contain a column named country_name along with the customer_id and first_name columns.
The value of country_name will be United States of America if the country is equal to USA.
Similarly, the value of country_name will be United Kingdom if the country is equal to UK.
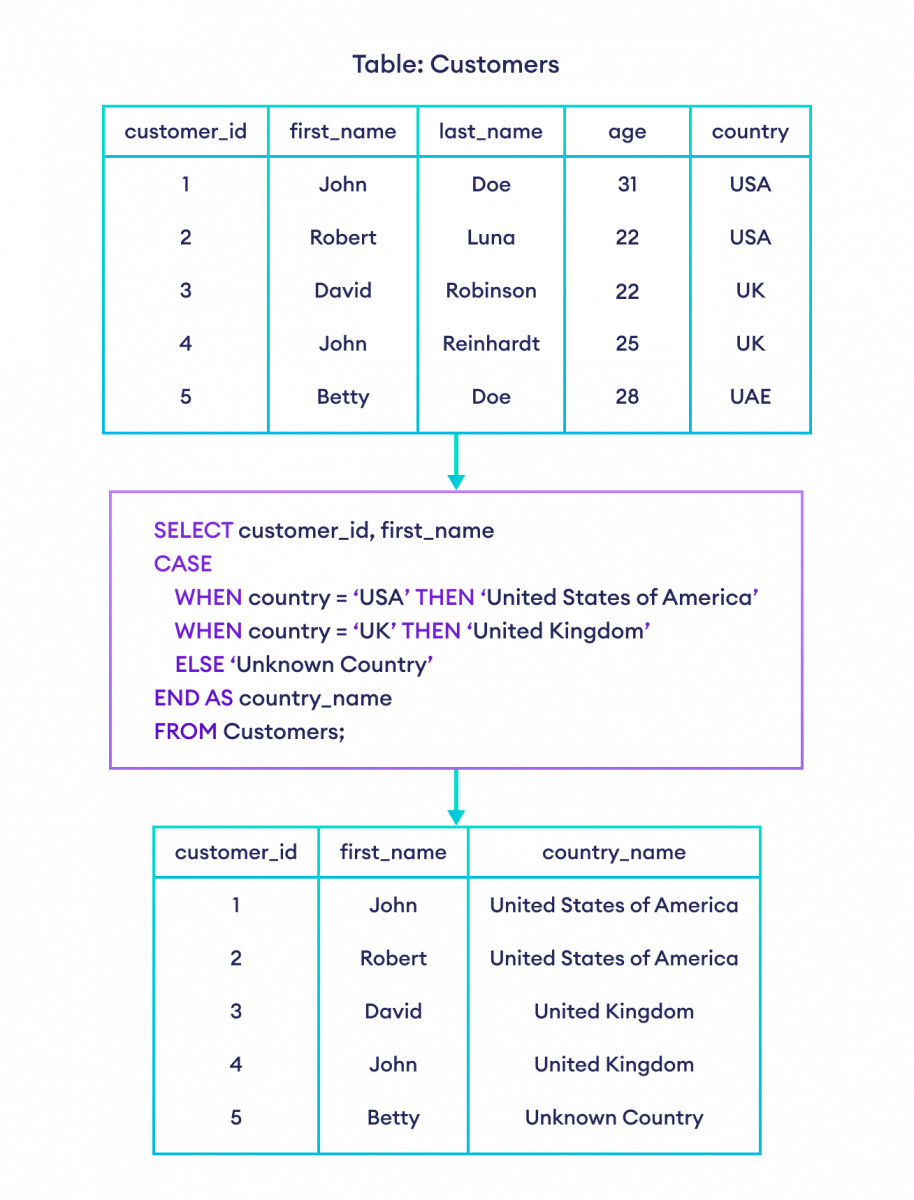
SQL CASE With ELSE
A CASE statement can have an optional ELSE clause. The ELSE clause is executed if none of the conditions in the CASE statement is matched.
For example,
-- CASE condition with ELSE clause in SQL
SELECT customer_id, first_name,
CASE
WHEN country = 'USA' THEN 'United States of America'
WHEN country = 'UK' THEN 'United Kingdom'
ELSE 'Unknown Country'
END AS country_name
FROM Customers;Here, the result set will contain a field named country_name along with customer_id and first_name.
The value of country_name will be:
- United States of America if the country is USA
- United Kingdom if the country is UK
- Unknown Country if the country is neither USA nor UK (because of the
ELSEclause).